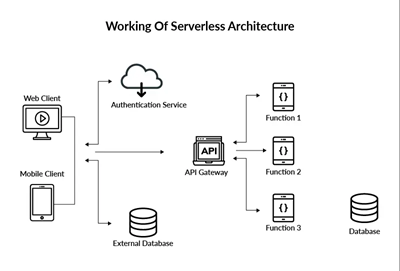
In the ever-evolving landscape of web development, scalability, flexibility, and resilience have become crucial factors for businesses to succeed. Traditional monolithic applications often struggle to meet these demands due to their rigid structure and complex interdependencies. Enter microservices architecture: a transformative approach to software development that breaks down applications into smaller, independent services.
What is Microservices Architecture?
Microservices architecture is a design paradigm where an application is composed of small, independent services that communicate with each other through well-defined APIs. Each service is focused on a specific business capability and can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. This modular approach contrasts sharply with the monolithic architecture, where all components are tightly coupled and must be deployed together.
Key Features of Microservices Architecture
- Decentralization:
- Microservices promote decentralization by allowing teams to choose the best tools, frameworks, and programming languages for their specific service.
- Independent Deployment:
- Each microservice can be deployed independently without affecting the rest of the system, reducing downtime and speeding up development cycles.
- Scalability:
- Microservices enable horizontal scaling. Services can be scaled individually based on demand, optimizing resource usage and costs.
- Resilience:
- The failure of one microservice doesn’t necessarily impact the entire application, improving overall system reliability.
- Continuous Delivery and Deployment:
- Teams can continuously integrate and deploy updates to individual services without disrupting the entire system.
Benefits of Microservices Architecture
- Improved Agility:
- Teams can work on different services simultaneously, accelerating development and innovation.
- Enhanced Fault Isolation:
- Issues in one service are contained and do not cascade through the system.
- Flexibility in Technology Stack:
- Developers can use diverse tools and technologies best suited for each service’s needs.
- Easier Maintenance:
- Small, focused services are easier to understand, update, and debug compared to monolithic applications.
Challenges and Considerations
While microservices offer numerous advantages, they come with their own set of challenges:
- Increased Complexity:
- Managing multiple services, each with its own database and dependencies, can be complex.
- Communication Overhead:
- Services must communicate over a network, introducing latency and potential points of failure.
- Deployment and Monitoring:
- Coordinating deployments and monitoring a distributed system requires robust tools and processes.
- Data Management:
- Ensuring data consistency across services can be challenging, especially in distributed environments.
Best Practices for Adopting Microservices
- Start Small:
- Begin by breaking off a few components of a monolithic application to create microservices.
- Invest in DevOps and Automation:
- Tools for CI/CD pipelines, containerization, and orchestration (e.g., Docker, Kubernetes) are essential.
- Embrace API Design:
- Well-defined and consistent APIs are critical for seamless communication between services.
- Implement Robust Monitoring:
- Use monitoring tools like Prometheus or Grafana to gain insights into service performance and health.
- Adopt a Resilient Architecture:
- Implement patterns like circuit breakers and retries to handle failures gracefully.